European patents are granted by the European Patent Office (EPO). The European Patent Office is situated in Munich and Berlin in Germany, in Vienna in Austria, in Brussels in Belgium and in the Hague in The Netherlands.

The European Patent Convention is a multinational convention of which 38 member states participate in, including all 28 member states of the European Union and 10 other non EU member states. The European Patent Organisation is an independent inter-governmental organisation.
Patent applications filed at the European Patent Office are prosecuted in a single official language, which can be either English, French or German and undergo a rigorous search and examination procedure.
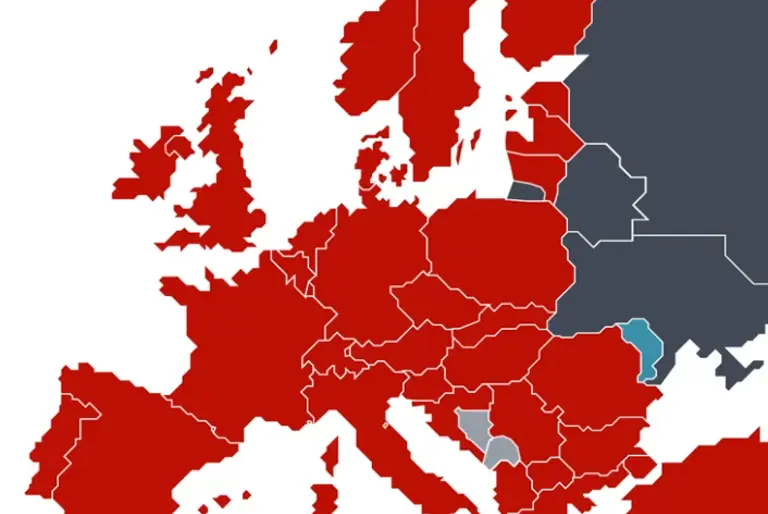
The following 39 countries are currently contracting states of the European Patent Convention (EPC):
(AL) Albania
(AT) Austria
(BE) Belgium
(BG) Republic of Bulgaria
(CH) Switzerland
(CY) Cyprus
(CZ) Czech Republic
(DE) Germany
(DK) Denmark
(EE) Republic of Estonia
(ES) Spain
(FI) Finland
(FR) France
(GB) United Kingdom
(GR) Hellenic Republic (Greece)
(HU) Hungary
(HR) Croatia
(IE) Ireland
(IS) Iceland
(IT) Italy
(LI) Liechtenstein
(LT) Lithuania
(LU) Luxembourg
(LV) Latvia
(MC) Monaco
(ME) Montenegro
(MK) Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia
(MT) Malta
(NL) Netherlands
(NO) Norway
(PL) Poland
(PT) Portugal
(RO) Republic of Romania
(RS) Serbia
(SE) Sweden
(SI) Slovenia
(SK) Slovakia
(SM) San Marino
(TR) Turkey
Further, European patents can be extended to:
(BA) Bosnia & Herzegovina
This extension state, whilst not having signed the European Patent Convention, has amended their national laws based on the European Patent Convention according to an agreement with the EPO.
There are also four validation states, being states which have signed a validation agreement with the EPO giving European patents effect in those states. These are:
(MA) Morocco; (MD) Republic of Moldova; (TN) Tunisia; (KH) Cambodia
European patents can be applied for by filing an application either directly at the European Patent Office in The Hague, Munich or Berlin, online, or via a local national receiving office, such as the UK Patent Office. European patents can also be obtained via an international patent application designating the European region.
The European Patent Office search procedure is highly respected for its thoroughness and quality. Typically a search may issue within around 4 to 18 months from filing.
The examination procedure before the European Patent Office is typically activated within 6 months to 2 years from filing. The examination procedure is somewhat lengthy, but is generally considered to be quite thorough. Patent applications are examined on the basis of novelty, inventive step and industrial applicability. There are some excluded classes of matter which are considered not to be inventions for the purpose of patentability. These include mathematical methods, methods of doing business, and scientific discoveries. However, even in these fields, patents have been granted for inventions which involve a technical contribution to the art.
European patent applications are highly cost-effective compared to the alternative of filing individual national patent applications in each state. Typically the cost of European patent application up to grant will be about the same as the cost of two individual national patent applications in EPC member states.
At the end of the patent application procedure, the European Patent Office grants a single European patent covering all designated states.
Once granted, the European patent is open to opposition from third parties for a period of 9 months. Simultaneously with the opposition period, generally within 3 months of grant, the patent must be "validated" to continue the rights for their maximum 20 year term from first filing date.
After grant, the European patent must be validated in each state in which rights are to be continued. For any states in which the national phase is not validated, protection lapses in that state after grant.
Renewal fees must also be paid in each national state for as long as the individual national phase patents are to remain in force.
For our foreign associates or direct clients, to file a European patent application we require your faxed, email or postal instructions detailing the following:
- name and address of the applicant (the owner of the rights);
- name and home addresses of each inventor;
- information as to how the applicants derived their rights in the invention (e.g. by virtue of employment of the inventors);
- a copy of specification, claims, abstract and formal drawings; and
- details of any priority claim: priority country, priority date and application number.
A power of attorney is required on filing or shortly after filing. No notarisation or legalisation of documents is required.
For further information, please read our white paper, which can be downloaded using the link at the bottom of this page or contact one of our European patent attorneys.